hcnak.blog
posted at 2019-09-15 17:48:55 +0000
微服务:Golang 实现简易RESTful服务
之前实现简单的API服务都是通过Python flask实现,最近由于工作需要,尝试了使用go实现。
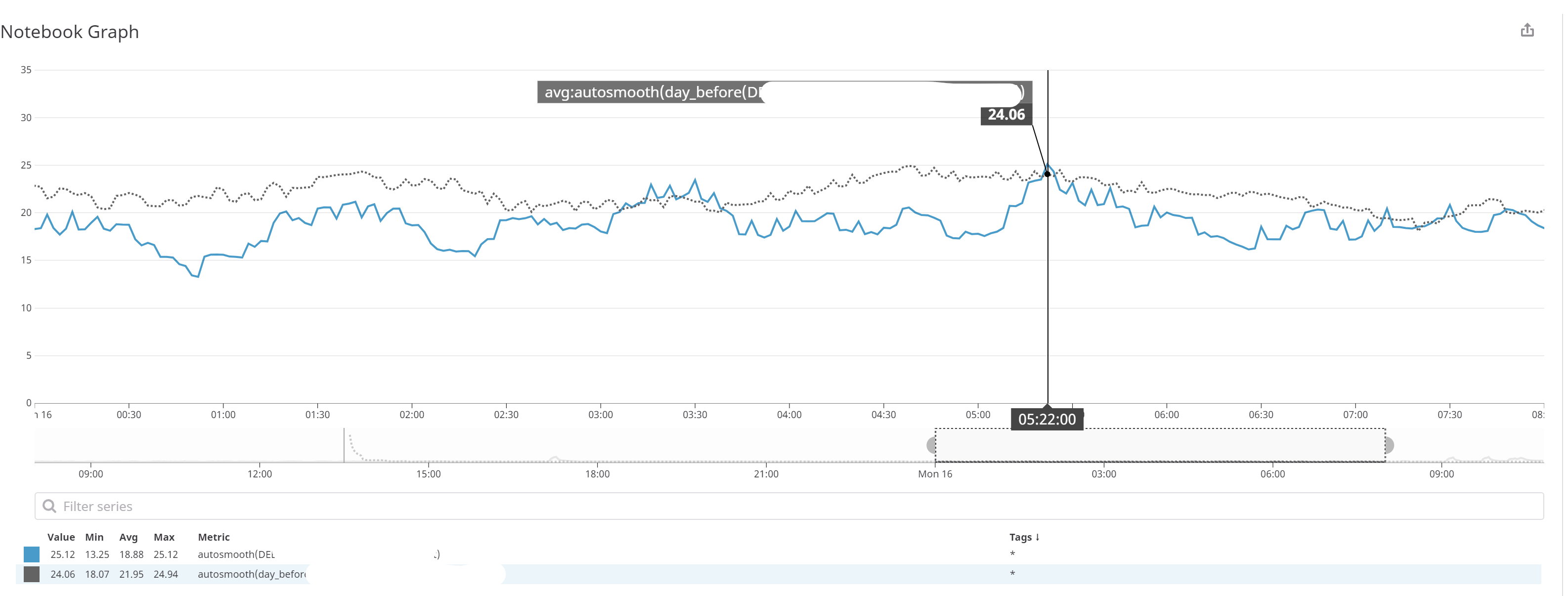
采用golang的原因是因为据说golang性能较python好,经过测试,golang性能的确较好:
测试方法为通过curl循环POST数据给给定地址。测试结果如下(虚线为python实现):
接下来我们讨论如何实现一个简单的go-restful。
假设我们要实现一个带有定时任务的RESTful服务,它可能定时去某一地方查询数据,然后进行某种处理,将处理后的数据提供给接口调用者。
我们主要会用到以下两个包:
我们通过restful.WebService来声明一个restful服务资源:
ws := new(restful.WebService)
然后我们便可以在该资源上设置资源路径,以及接受和产生数据的MIME类型:
ws.Path("/postjob").
Consumes(restful.MIME_JSON).
Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
紧接着我们可以给访问该资源的不同HTTP请求指定处理函数
简单的通过_ws.Route(ws.METHOD("/PATH").To(PROCESS_FUNC))_实现:
ws.Route(ws.POST("/").To(postJob)) //这里POST的路径是相对于ws的Path的
于是,我们便有了一个完整的微服务资源定义:
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/postjob").
Consumes(restful.MIME_JSON).
Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.POST("/").To(postJob))
定义资源后,我们需要注册资源以便使用它:
restful.Add(ws)
最后,启动服务即可:
http.ListenAndServe(":5000", nil) //默认为0.0.0.0:5000
//log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":5000", nil)) <-- 这样写以便输出日志
为了使用方便,在实际使用中,我们可以将各个资源定义写成函数(如同Java里的资源类),然后在go的主函数体中完成资源的注册与服务器启动:
func main() {
restful.Add(sampleResource())
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":5000", nil))
}
func sampleResource() *restful.WebService {
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/postjob").
Consumes(restful.MIME_JSON).
Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.POST("/").To(postJob))
return ws
}
完整源代码如下
package main
import (
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/carlescere/scheduler"
"github.com/emicklei/go-restful"
)
func main() {
scheduler.Every(3).Minutes().Run(scheduledJob) //定时任务
restful.Add(resetfulService())
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":5000", nil))
}
func resetfulService() *restful.WebService {
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Path("/postjob").
Consumes(restful.MIME_JSON).
Produces(restful.MIME_JSON)
ws.Route(ws.POST("/").To(postJob))
return ws
}
func scheduledJob() { //定时任务函数
// do something here
}
func postJob(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response){
// do something with HTTP POST method
}
参考
- package restful
- package scheduler
- Build and Deploy a secure REST API with Go, Postgresql, JWT and GORM
© kanch → zl AT kanchz DOT com
last updated on 2022-07-27 01:57:54 +0000